Understanding DHCP: How Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Works and Its Benefits

DHCP stands for what?
Knowing the words behind this term, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, helps one to clearly grasp DHCP. That seems difficult, but fundamentally it is not. DHCP, then, is a client-server network management tool handling automatic assignment of network configuration settings including IP address, netmask, gateway, DNS servers. Stated differently, DHCP is the mechanism enabling your device to have internet connection immediately following router connectivity running a DHCP server.
How does DHCP function?
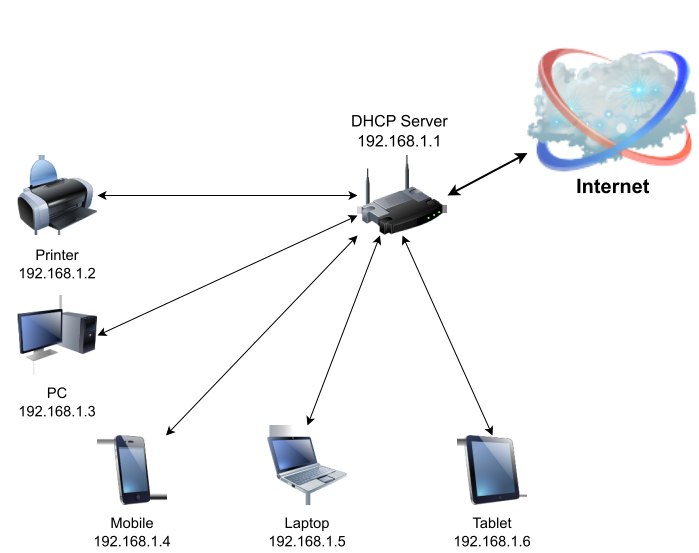
Requested from the client-side device, DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) operates in many cases—that of your laptop or mobile phone, printer or any other Internet-supporting device you could have. Your device has to have a DHCP client service turned on if settings exchange is to take place so that a DHCP request may be published in the network just connected to. For instance, if DHCP is turned on for the adapter in use when you plug in a LAN cable in your laptop, a DHCP protocol broadcast request will be sent in that local network when authenticating with a WiFi network or right after that. The DHCP server, for instance your router that manages your local network and the WiFi as well, would see that broadcast request and if it has been set to provide configuration information using that protocol, it would react with the information your device needs in order to acquire Internet access and connectivity in the network managed by the router.
The response would comprise the so-called DHCP options:
DHCP Policies
Eventually the client should configure for the network adapter in use, so the set of configuration choices delivered from the server to the client should reflect this.
The suggested IP address your gadget should assign as a private IP
The Netmask or Subnet/CIDR you need set to enable connectivity between your IP and the gateway to operate.
DNS server(s) to be configured so that, necessary for any Internet access, you might translate domains into IP addresses
Since the DHCP Options must be renewed, the actual DHCP Server’s IP address is needed.
The Lease Time is the period following which the client should ask another question to find out whether the network configuration should be kept the same or changed.
DHCP Devices
What is a DHCP server?
Basically, a DHCP server is a network-connected routing device that is not always but typically your router utilised finally as the gateway address for Internet connectivity. In the same network the DHCP server and the clients are connected to, the server manages and automatically allocates IP addresses to the clients that seek TCP/IP configuration information from it. It is pre-configured with the netmask that clients must use, the IP of the default routing gateway and optionally DNS server addresses used for name resolution, the IP ranges also known as IP Address Pool that the DHCP server is permitted to supply and issue. Usually housed on routers acting as gateways, DHCP servers can alternatively run on another device.
What is a client for DHCP?
That can be any kind of gadget with network capabilities: computers, laptops, mobile phones, printers, scanners, IoT devices, IP cameras, Smart TVs and others. They are DHCP clients since they have a DHCP client service running used to request and set a specific network adapter with the settings (Options) supplied by the DHCP Server.
DHCP Leases Time
The DHCP Lease Time given by DHCP Servers is a number in seconds that indicates the advised to the client time immediately following which the DHCP Client should seek fresh or renewed DHCP Options from the Server. That operation is to ensure that configuration such IP addresses is kept current and accurate according to the settings pre-set in the server in order to keep the client network organised and functional and to avoid IP conflicts.
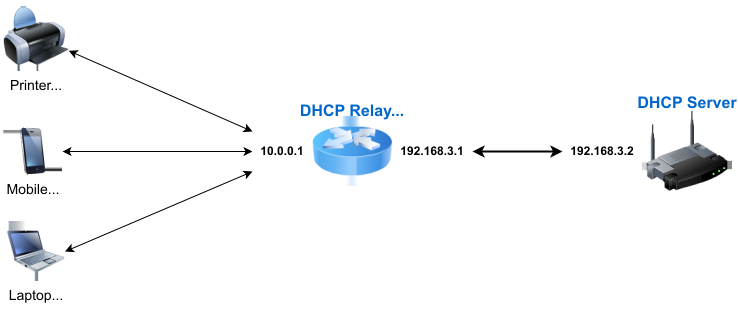
DHCP Relay Agent Program
DHCP relay agents are routing devices used in some network configurations to transparently transport requests and responses between the clients and the DHCP server therefore enabling successful configuration sets to be exchanged. Acting as a middleman between the client device and the server, such a relay agent
Benefits of utilising DHCP Efficiency: This protocol guarantees that configuration is being transferred without the need of the people in demand of connectivity to be computer smart or to undertake difficult manual configuration activities on their devices in order to gain Internet Access.
It allows network managers to segment and arrange their networks so that distinct groups of customers depending on different criteria can be mapped and assigned IP addresses inside certain IP ranges (ip address pool).
DHCP makes automatically reliable IP address setup of all DHCP-enabled clients whenever it is required for new IP address ranges used locally or the default gateway or DNSes to be changed. Not to mention hassle-free client-side seamless functionality, that yields time savings and cost-efficiencies.
Should one assume that every client in the network is using the DHCP Service, the server guarantees that no two or more network devices share the same IP address.
Should DHCP be in or out of use?
DHCP should be turned on for your network adapter in use if you would need your client device to automatically obtain the network configuration automatically without the help of a network administrator; e.g., if you have no idea what the gateway is, what IP addresses are allowed to be set in the specific network you have connected to, or if you should use the local DNS server instead of publicly available ones which can sometimes be filtered.
The IP address of the default gateway, the subnet mask, and you either can use the gateway as a DNS or have external DNS servers unfiltered and available – then you can switch DHCP off if you need a static local IP address which does not change every time you re-connect to the network in use and you are confident you know what IP addresses are allowed connectivity.
DHCP against a static IP address
The DHCP Protocol’s name consists of the word dynamic, so you can hypothesise and be right to think that by using a DHCP client you acquire dynamic IP addresses, which would most likely change over time or whenever you disconnect and reconnect to a given network. While being handy would not allow one to take advantage of the benefits of static IP addresses, which can be but are not limited to port forwarding, QoS, and such. Remember that using DHCP does not always mean that every time your device connects to the network it would acquire a different IP address. A DHCP server allows network managers to assign a specific valid IP address to a given MAC address, therefore providing a unique identification of every network adapter, such a LAN adapter or a WiFi adapter.
Pro-Tip: Should the DHCP protocol exchange in responsibility of assigning IP addresses fail due to misconfiguration from either the client or the server side, Internet Connectivity is sometimes constrained. This is why try manually assigning an IP from some of the typical private IP address ranges with their associated regularly used gateway IP address and subnet mask when you join to a LAN network and you observe that your adapter has no TCP/IP
configuration configured. Among those are some:
Source: 192.168.0.0
Gateway: 192.168.0.1 IP Address: 192.168.0.2-254
255.255.255.0 is Netmask.
IP Address: 10.0.0.2-254 Gatekeeper: 10.0.0.1 or 10.0.0.0.1 Network
Netmask:255.255.255.0
IP address: 192.168.1.2-254; gatekeeper: 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.l.l
255.255.255.0 netmask
Although the network in issue has a DHCP server turned on, this does not always mean you have to utilise it to enable Internet connectivity and/or routing via the default gateway. Moreover, if you have access to your router administrative panel, you may change, turn on, off the DHCP server capability.
Useful DHCP Resources
From The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), the entity that standardised the dynamic host configuration protocol as a replacement of the bootstrap protocol (BOOTP):
DHCP: rfc2131 HTML document available at https://datatracker.ietf.org
Relay Agent: rfc3046 HTML doc @ https://datatracker.ietf.org
Network Attachment: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc4436
Copyright © 2025 routeripnet.com
